-
Research Article
-
Exploring Geographical Approaches to ‘World Climate’ Learning in Elementary Schools
초등학교 ‘세계의 기후’ 학습에 대한 지리교육적 방향 탐색
-
HyunJu Kim
김현주
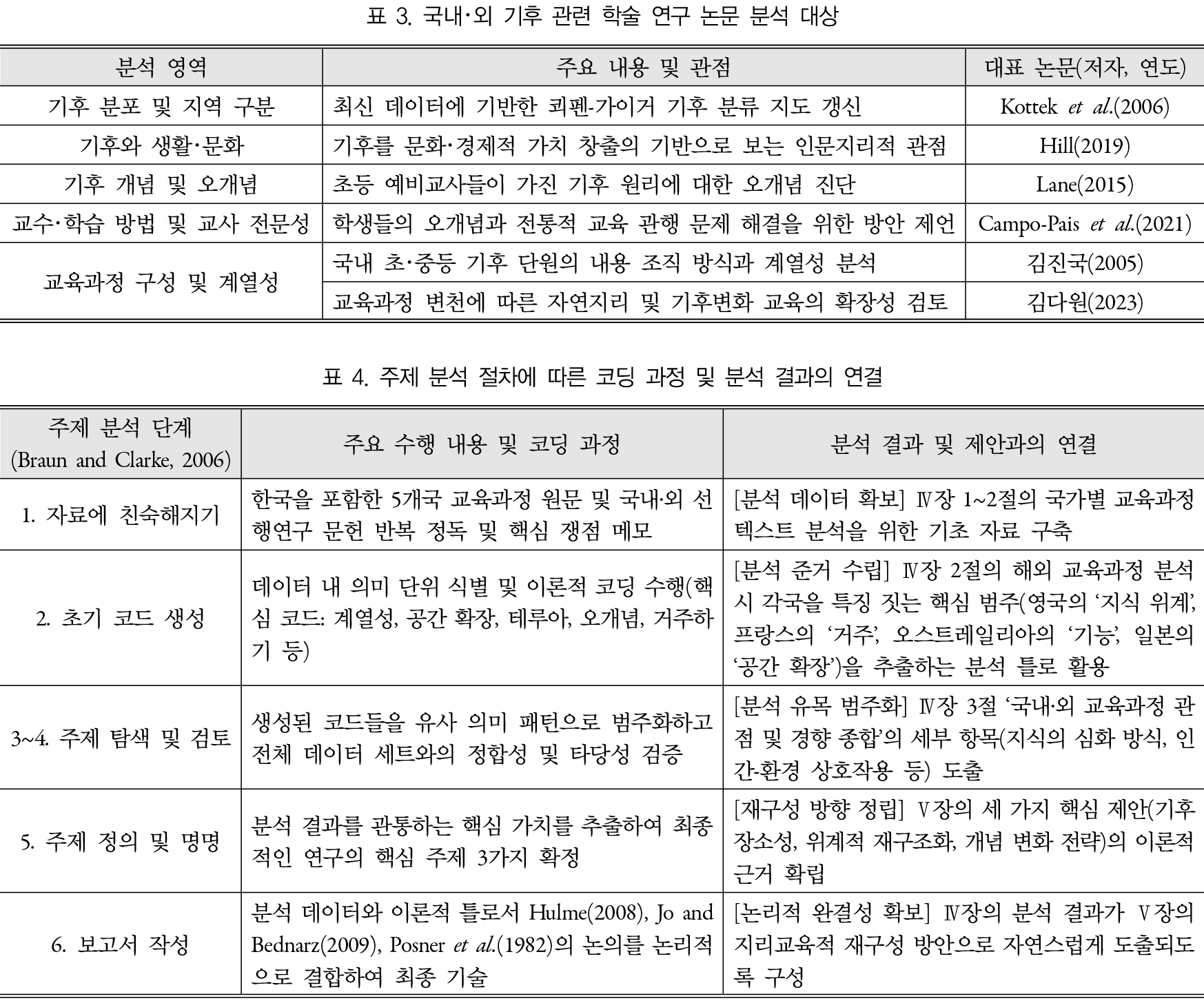
- This study aims to seek the direction for the development of ‘World Climate’ education, a key subject in primary geography education. Currently, …
본 연구는 초등 사회과 지리 영역의 핵심 주제인 ‘세계의 기후’ 교육이 나아가야 할 방향을 모색하는 데 목적이 있다. 한국의 현행 ‘세계의 기후’ …
- This study aims to seek the direction for the development of ‘World Climate’ education, a key subject in primary geography education. Currently, Korean education emphasizes the classification of climatic zones and spatial distribution, often presenting the relationship between climate and human life through a linear perspective. Recognizing these limitations, this study analyzed the curricula and academic literature of the United Kingdom, France, Australia, and Japan to explore alternative approaches. The findings indicate that these countries systematically structure their curricula by connecting climate to concepts such as human-nature interactions and ‘habiter’. Additionally, relevant research highlights the importance of exploring the cultural values of climate and implementing pedagogical strategies to address learners’ misconceptions. Based on these findings, this study proposes three directions for improvement. First, it suggests introducing the concept of Climate Placeness, which understands climate as a foundation of life and place identity. Second, it recommends restructuring learning contents hierarchically by considering spatial concepts, representational tools, and reasoning processes. Third, it emphasizes teaching and learning strategies that respect students’ misconceptions as alternative frameworks and promote conceptual change through cognitive conflict. The findings of this study contribute to enhancing students’ geographical literacy and to transforming world climate learning into meaningful education that enables learners to explore the relationship between climate and human life in a multidimensional way.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 초등 사회과 지리 영역의 핵심 주제인 ‘세계의 기후’ 교육이 나아가야 할 방향을 모색하는 데 목적이 있다. 한국의 현행 ‘세계의 기후’ 교육은 기후대 구분 및 공간적 분포 파악을 중시하며, 기후와 인간 생활의 관계를 단선적으로 설명하는 경향이 있다. 이에 본 연구는 현행 교육과정의 한계를 보완할 수 있는 대안적 접근을 탐색하고자 영국, 프랑스, 오스트레일리아, 일본의 교육과정 및 관련 학술 연구 문헌을 분석하였다. 분석 결과, 해외 주요국의 교육과정은 기후를 자연과 인간의 상호작용 및 ‘거주하기’ 등의 개념과 연계하여 체계적으로 조직하고 있었으며, 학술 연구에서는 기후의 문화적 가치 탐구와 학습자 오개념에 대한 교수학적 접근 등을 강조하고 있었다. 이를 토대로 본 연구는 세 가지 개선 방안을 제안한다. 첫째, 기후를 삶과 장소의 정체성으로 이해하는 ‘기후 장소성’ 개념의 도입이다. 둘째, 공간 개념, 표상 도구, 추론 과정을 고려한 학습 내용의 위계적 재구조화이다. 셋째, 학습자의 오개념을 대안 개념으로 존중하고 인지적 갈등을 통해 과학적 개념으로 변화시키는 교수·학습 전략의 적용이다. 본 연구의 논의는 초등학교 ‘세계의 기후’ 학습이 학습자의 지리적 소양을 함양하고, 기후와 인간의 관계를 입체적으로 탐구하는 실질적인 교육으로 거듭나는 데 기여할 것이다.
-
Exploring Geographical Approaches to ‘World Climate’ Learning in Elementary Schools
-
Research Article

-
Characteristics of the ‘Geography’ Subject in Japan’s 2018 Revised High School Curriculum Guidelines and Textbook - Focusing on the Geography-based Epistemological Approaches -
일본의 2018년 개정 고등학교 학습지도요령 및 교과서에서 ‘지리총합’ 과목의 성격 - ‘지리적으로 보는 법·생각하는 법’을 중심으로 -
-
Byung-il Yang
양병일
- This study aims to clarify the characteristics of Geography subject, which was newly established and mandated in the Geography and History department …
본 연구의 목적은 2018년 개정 일본 고등학교 학습지도요령 지리역사과에 신설 및 필수화된 지리총합 과목의 성격을 규명하는 것이다. 이를 위해 일본 지리교육의 영역 …
- This study aims to clarify the characteristics of Geography subject, which was newly established and mandated in the Geography and History department of the 2018 revised Japanese High School Curriculum Guidelines. For this purpose, geography-based epistemological approaches was used as the analytical framework. Based on this framework, the study examined the curriculum structure and the implementation methods in textbooks, focusing on the National Curriculum Guidelines and the Tokyo-Shoseki textbook. The research findings are as follows. First, Geography positions geography-based epistemological approaches as a core mechanism that integrates the elements of qualities and abilities. Second, the Curriculum Guidelines and textbook for Geography feature a systematic and progressive structure that begins with the acquisition of geographical skills, moves through global-scale inquiries, and leads to local field investigations in daily life zones. Third, the Geography textbook has shifted away from a dictionary-like structure centered on academic definitions, strengthening its character as a methodological guide that presents abundant case studies and Web GIS applications. These analytical results provide significant implications as foundational data for establishing the identity of the geography curriculum and developing textbooks in South Korea in the future.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구의 목적은 2018년 개정 일본 고등학교 학습지도요령 지리역사과에 신설 및 필수화된 지리총합 과목의 성격을 규명하는 것이다. 이를 위해 일본 지리교육의 영역 특수적 사고인 ‘지리적으로 보는 법·생각하는 법’을 분석 틀로 설정하고, 학습지도요령과 도쿄쇼세키(東京書籍) 교과서를 중심으로 교육과정의 구조와 교과서의 구현 방식을 고찰하였다. 연구 결과는 다음과 같다. 첫째로 지리총합 과목은 ‘지리적으로 보는 법·생각하는 법’을 자질·능력의 요소를 통합하는 핵심 기제로 설정하고 있다. 둘째로 지리총합 과목의 학습지도요령과 교과서는 지리적 기능 습득에서 시작해 세계적 규모의 탐구를 거쳐 생활권 지역조사로 이어지는 계통적이고 점진적인 심화 구조를 갖추고 있다. 셋째로 지리총합의 교과서는 학술적 정의 중심의 사전적 구성에서 벗어나 풍부한 사례와 웹GIS 활용법을 제시하는 방법론적 가이드북으로서의 성격이 강화되었다. 이러한 분석 결과는 향후 우리나라 지리 교육과정의 정체성 확립 및 교과서 개발을 위한 기초 자료로써 중요한 시사점을 제공한다.
-
Characteristics of the ‘Geography’ Subject in Japan’s 2018 Revised High School Curriculum Guidelines and Textbook - Focusing on the Geography-based Epistemological Approaches -
-
Research Article

-
Learners’ Perceptions of the Climate Crisis in an Integrated Social Studies 1 Learning Activity - An Analysis of Climate Fiction Outlines -
통합사회1 학습 활동에서 나타나는 학습자의 기후위기 인식 특성 - 기후소설 개요 분석을 중심으로 -
-
Jihyun Tae
태지현
- This study explores learners’ perceptions of the climate crisis by analyzing a “climate fiction outline writing” activity designed in accordance with the …
본 연구는 2022 개정 교육과정 「통합사회1」의 ‘자연환경과 인간’ 영역 성취기준을 바탕으로 설계한 ‘기후소설 개요 작성’ 활동을 분석하여 학습자의 기후위기 인식 특성을 탐구하였다. …
- This study explores learners’ perceptions of the climate crisis by analyzing a “climate fiction outline writing” activity designed in accordance with the achievement standards of the “Natural Environment and Humans” unit in the 2022 Revised National Curriculum for Integrated Social Studies 1. Learners’ narratives were analyzed using a three-stage framework of understanding, action, and reflection. In the understanding stage, learners framed the climate crisis as a structural issue linked to inequality and institutional responsibility, though spatial settings were largely symbolic. In the action stage, responses expanded from individual efforts to collective and institutional measures, including technological solutions; however, these were often presented in parallel without clear spatial contexts of transition. In the reflection stage, themes of climate anxiety and responsibility emerged, with some narratives critically addressing power dynamics and the distribution of responsibility. These findings reveal the limitations of abstract, globalized climate education and highlight the need for place-based approaches connected to learners’ lived experiences.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 2022 개정 교육과정 「통합사회1」의 ‘자연환경과 인간’ 영역 성취기준을 바탕으로 설계한 ‘기후소설 개요 작성’ 활동을 분석하여 학습자의 기후위기 인식 특성을 탐구하였다. 이 과정에서 소설의 구성 요소를 ‘이해–실천–성찰’의 분석 틀에 따라 해석하였다. 이해 단계에서 학습자는 기후위기를 불평등과 제도적 책임이 결합된 사회구조적 문제로 인식하였으나, 공간 설정은 상징화된 지역에 집중되는 경향을 보였다. 실천 단계에서는 기후위기 대응을 공동체, 제도 개선 및 기술적 해결로 확장하였으나, 해결 방식은 병렬적으로 제시되었고 전환의 구체적 공간과 실행 맥락은 충분히 드러나지 않았다. 성찰 단계에서는 기후 불안과 책임 의식이 나타났으며, 일부는 이를 권력과 책임 분담의 문제로 확장하였다. 특히 전환이 이루어지지 않은 결말은 기후위기를 불확실성과 한계를 동반한 장기적 과제로 인식하고 있음을 보여주었다. 이는 기후위기를 지구적 차원의 추상적 담론 중심으로 다루어 온 기존 교육의 한계와 관련되며, 향후 기후위기 교육이 학습자의 생활세계와 밀접한 장소적 맥락 속에서 재구성될 필요가 있음을 시사한다.
-
Learners’ Perceptions of the Climate Crisis in an Integrated Social Studies 1 Learning Activity - An Analysis of Climate Fiction Outlines -
-
Research Article
-
Exploring a Research-Based Praxis Model in Geography Education for the Realization of Critical Global Citizenship - A Case Study of a Graduate Course on “Global Citizenship and Geography Education” -
비판적 세계시민성 구현을 위한 지리교육의 연구 기반 실천 모형 탐색 - ‘세계시민과 지리교육’ 대학원 강좌 사례 -
-
Yeongwoo Beom · Kyonghwan Park · Su-Jeong Kim
범영우 · 박경환 · 김수정
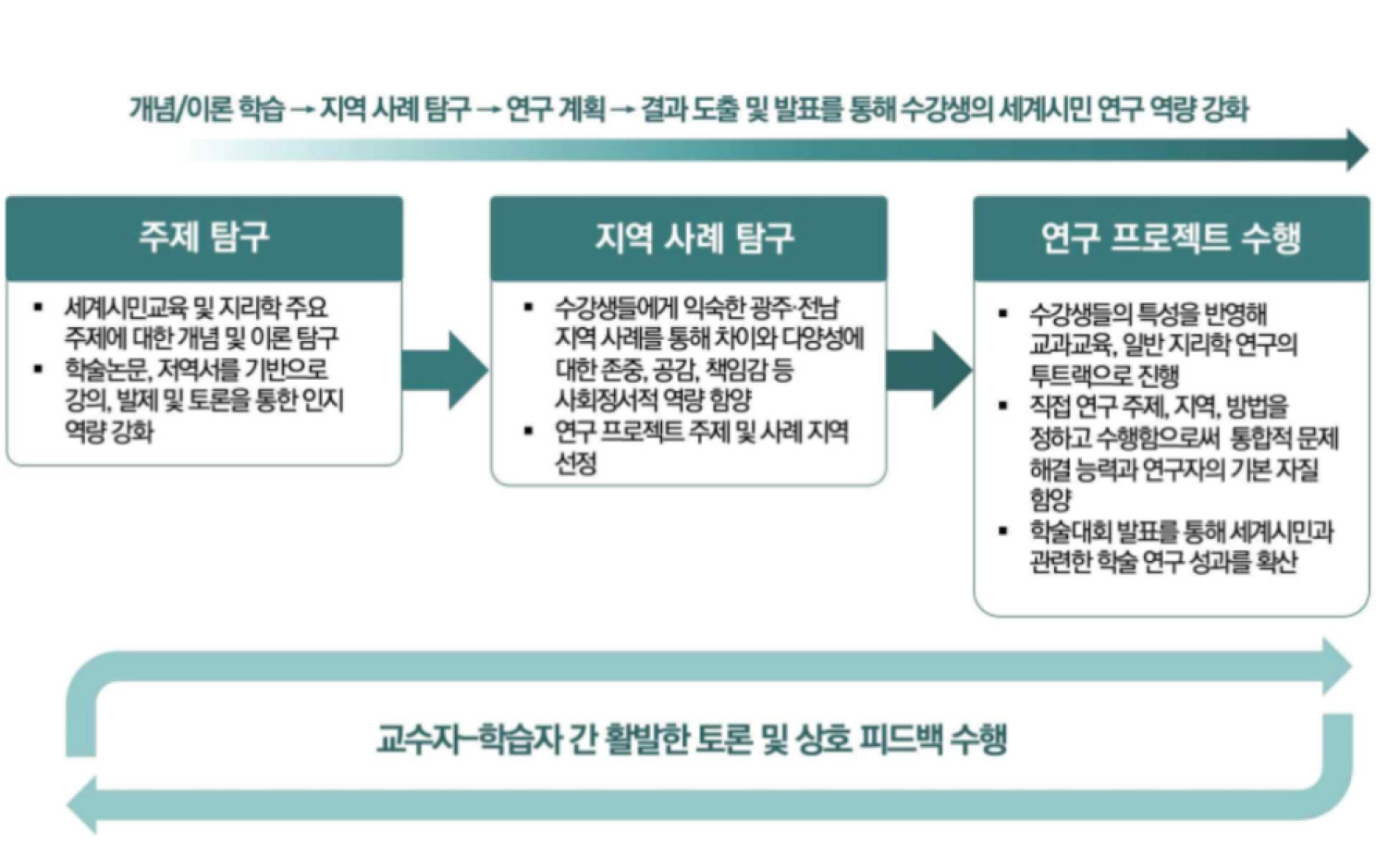
- As globalization intensifies and transnational challenges proliferate, geography education is well positioned to advance critical global citizenship by fostering multi-scalar and relational …
최근 세계화의 심화와 초국경적 문제의 확산 속에서 단일 국가 중심의 시민 개념을 넘어서는 비판적 세계시민성 함양이 중요한 교육적 과제로 부상하고 있다. 지리교육은 …
- As globalization intensifies and transnational challenges proliferate, geography education is well positioned to advance critical global citizenship by fostering multi-scalar and relational thinking that foregrounds power and inequality. This article presents a case study of a graduate-level course, “Global Citizenship and Geography Education,” offered in a Department of Geography Education at a national university in South Korea. Designed around project-based learning, the course begins with local community issues, traces their connections to wider socio-spatial structures, and develops these issues into researchable questions within critical global citizenship education. We examine how the course framed global citizenship not simply as a set of values to transmit, but as an object of geographical enquiry to be investigated and reworked through disciplinary concepts and methods. The staged sequence - from topic generation and theoretical reframing to analysis and academic presentation- illustrates one pathway for linking geographical enquiry with research-based praxis in geography education. This case suggests that carefully structured project-based learning can support the integration of critical global citizenship across research and teaching in geography education.
- COLLAPSE
최근 세계화의 심화와 초국경적 문제의 확산 속에서 단일 국가 중심의 시민 개념을 넘어서는 비판적 세계시민성 함양이 중요한 교육적 과제로 부상하고 있다. 지리교육은 다중 스케일 사고와 공간적 관계 분석을 통해 세계적 의제를 구조적으로 이해하도록 돕는 학문적 기반을 지니지만, 이를 연구와 수업 실천의 차원에서 체계적으로 조직하려는 시도는 아직 충분히 축적되지 않았다. 본 연구는 「세계시민과 지리교육」이라는 대학원 강좌를 사례로 하여, 비판적 세계시민성을 연구 주제로 조직하고 실천과 연결한 강좌 설계의 특징과 그 지리교육적 함의를 고찰한다. 해당 강좌는 수강생이 지역사회 현안을 출발점으로 다중 스케일 속에서 글로벌 구조를 재해석하고 이를 비판적 세계시민성의 관점에서 연구 문제로 전환하도록 조직되었다. 이 과정에서 세계시민성은 가르쳐야 할 가치가 아니라, 지리적 개념과 방법론을 통해 분석되고 재구성되는 탐구 대상으로 자리매김하였다. 강좌는 연구 주제 생성–이론적 재맥락화–자료 분석–학술 산출로 이어지는 단계적 구조를 통해 세계시민교육을 지리교육의 공간 개념 및 탐구 방법론과 긴밀히 연결하였다. 이는 일반적인 자기주도 연구 수행을 넘어, 지역 기반 사례를 글로벌 맥락 속에 위치시키고 비판적 세계시민성을 지리적 사고로 재구성하도록 설계되었다는 점에서 특징적이다. 본 사례는 프로젝트기반학습이 비판적 세계시민성을 학문적 연구와 교육 실천의 연속선상에서 통합적으로 구현하는 매개 장치로 기능할 수 있음을 보여준다.
-
Exploring a Research-Based Praxis Model in Geography Education for the Realization of Critical Global Citizenship - A Case Study of a Graduate Course on “Global Citizenship and Geography Education” -
-
Research Article
-
A Literature Review on Thematic Analysis of Elementary Environmental and Ecological Education Programs
초등 환경·생태교육 프로그램에 관한 주제분석적 문헌고찰
-
Youjin Hong · Jeanyoung Kim
홍유진 · 김진영
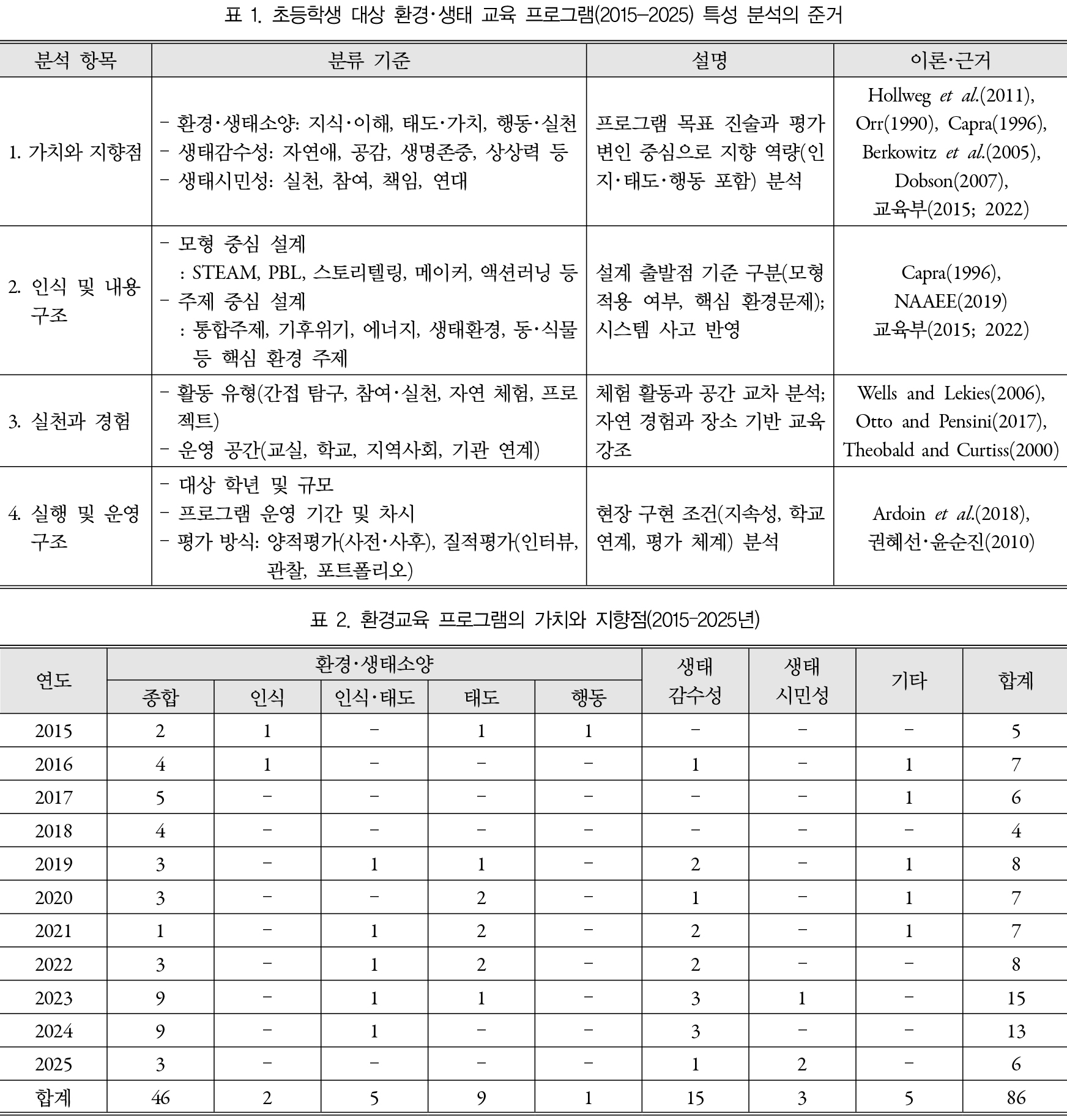
- This study systematically analyzed 86 elementary environmental and ecological education programs implemented in Korea between 2015 and 2025, employing a four-dimensional framework …
본 연구는 2015년부터 2025년까지 수행된 국내 초등 환경·생태교육 프로그램 86편을 대상으로 가치와 지향점, 내용 구조, 실천과 경험, 실행·운영 구조의 4차원 준거에 따라 …
- This study systematically analyzed 86 elementary environmental and ecological education programs implemented in Korea between 2015 and 2025, employing a four-dimensional framework encompassing values and orientation, content structure, practice and experience, and implementation and operational structure. The findings indicate that Korean elementary environmental and ecological education programs have accumulated evidence of effectiveness primarily centered on fostering environmental–ecological literacy, while more recent programs show a gradual expansion of objectives toward ecological sensitivity and citizenship. In terms of content structure, instructional model–driven reconfiguration was prominent, with integrated, experiential, and STEAM-based convergence programs constituting the dominant approaches. At the level of practice and experience, activity-based instruction was widely adopted; nevertheless, learning experiences tended to remain concentrated in classroom-based indirect inquiry, with limited extension into community contexts and students’ everyday life-worlds. Regarding implementation and operational structure, programs were largely concentrated in upper grades, implemented over mid- to long-term duration, and predominantly reliant on quantitative evaluation methods, while vertical articulation across grade levels was largely absent. By applying a four-dimensional analytical framework, this study provides an integrated perspective on program goals, content, experiential design, and operational conditions, and offers structural implications for advancing the practical design of ecological transformation education at the elementary level.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 2015년부터 2025년까지 수행된 국내 초등 환경·생태교육 프로그램 86편을 대상으로 가치와 지향점, 내용 구조, 실천과 경험, 실행·운영 구조의 4차원 준거에 따라 체계적으로 분석하였다. 분석 결과, 국내 초등 환경·생태교육 프로그램은 환경·생태소양 함양을 중심으로 효과성 검증을 축적해 왔으며, 최근에는 생태감수성과 시민성으로 목표가 점진적으로 확장되는 경향을 보였다. 내용 구조에서는 교수·학습 모형 중심의 재구성이 두드러졌으며, 통합형·생태체험형·STEAM 기반 융합형 프로그램이 주류를 이루었다. 실천과 경험 차원에서는 활동 중심 수업이 일반화되었으나, 실제 경험은 교실 기반 간접 탐구에 집중되는 경향이 강했으며, 지역사회 및 생활세계로 확장된 실천은 제한적이었다. 실행·운영 구조는 고학년 집중, 중·장기 운영, 양적 평가 중심의 특성을 보였고, 학년 간 연계 설계는 거의 이루어지지 않았다. 본 연구는 4차원 분석 틀을 통해 프로그램의 목표, 내용, 경험, 운영 조건을 통합적으로 조망함으로써 향후 초등 생태전환교육의 실천적 설계 방향을 제시했다는 점에서 의의를 가진다.
-
A Literature Review on Thematic Analysis of Elementary Environmental and Ecological Education Programs
Journal Informaiton
 The Journal of The Korean Association of Geographic and Environmental Education
The Journal of The Korean Association of Geographic and Environmental Education
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 The Journal of The Korean Association of Geographic and Environmental Education
The Journal of The Korean Association of Geographic and Environmental Education










